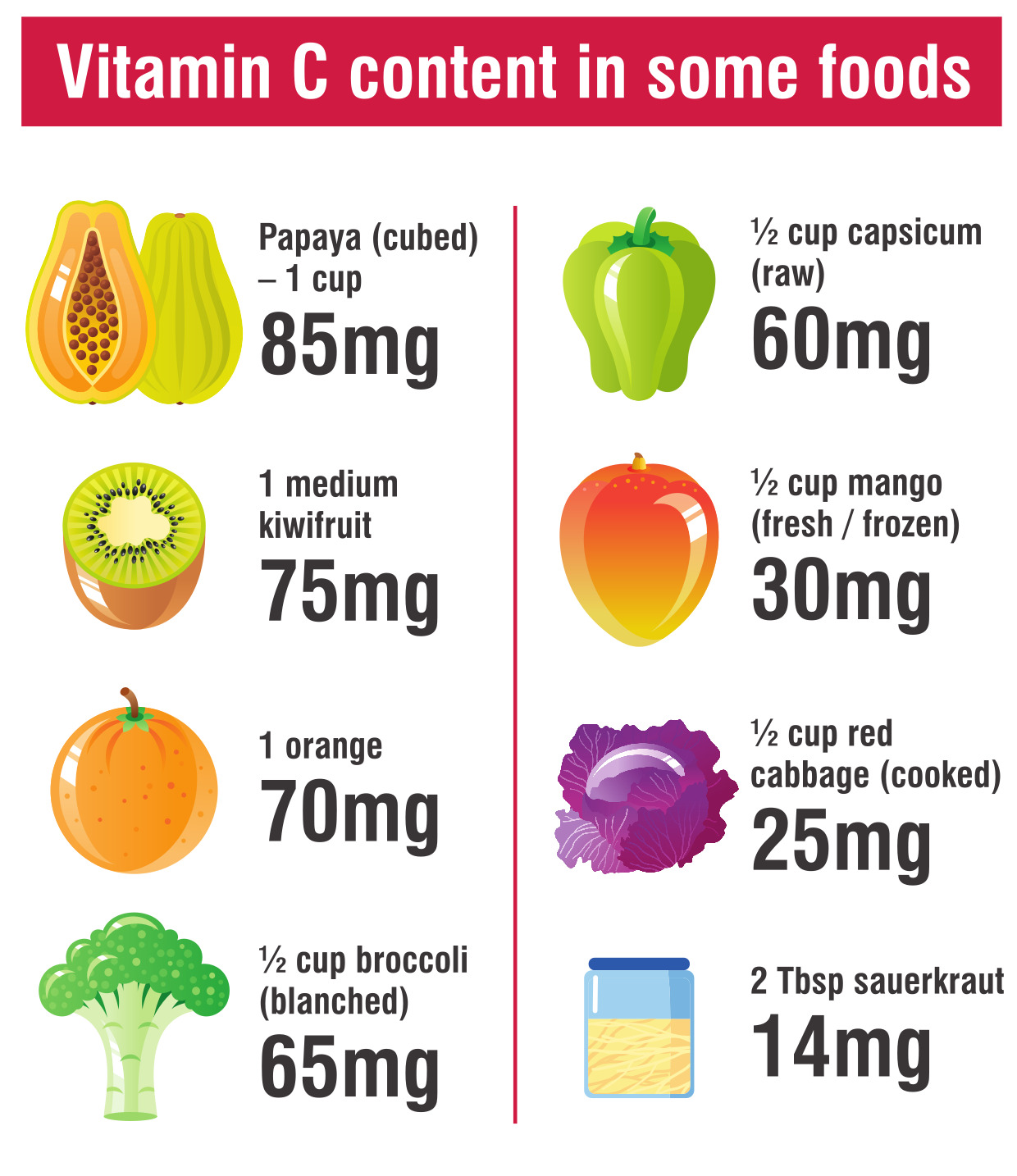
It plays an important role in the production of neurotransmitters, collagen production, as well as being a co-factor in various enzymes responsible for energy production.

Vitamin C absorption takes place in the small intestine. Intestinal dysfunction may reduce absorption, therefore if you have been diagnosed with Coeliac disease or experience IBS or other conditions associated with the digestive tract, you may be low in this nutrient.
Small frequent doses of vitamin C from food and supplements appear more efficacious than large doses. Low doses of 200-400mg results in 100% absorption, however if 500mg is exceeded, bioavailability reduces, decreasing to approximately 30% when 1000mg is consumed orally in one bout. This is due to maximal saturation of the intestinal transporter called SVCTI.
Iron absorption is dependent on vitamin C although human clinical trials have not yet proven iron with vitamin C in a supplement to be superior to iron supplementation alone for anaemic patients. This may be because an ascorbic acid-to-iron molar ratio of 2:1 is necessary to increase iron bioavailability and most studies do not meet this.
In individuals with diabetic foot ulcers, vitamin C (as ascorbic acid) (500mg/day for 8 weeks) was shown to increase wound healing compared to controls. The vitamin C group recorded no amputations compared to 5 amputations seen in the control group.

The benefits of vitamin C are enhanced when used in combination with bioflavonoids compared to the use of vitamin C alone so if looking for a supplement, choose one with bioflavonoids present.
 Photo: Getty Images
Banana and kiwi parfait
Photo: Getty Images
Banana and kiwi parfait

Ingredients
1 medium banana
½ cup plain Greek yoghurt or coconut yoghurt
1 Tbsp hemp seeds
½ tsp vanilla extract
2 Tbsp raw almonds, roughly chopped
1 kiwifruit, peeled and diced
Mash banana with a fork and add to yoghurt, hemp seeds and vanilla extract. Mix well.
Place into a decorative glass (or container to take to work).
Top with kiwifruit and then almonds and enjoy.