

This means it is very bright. The planet clears the northeastern horizon just after 8pm. By the time the sky darkens, Mars will be easily visible as a blazing orange/red "star".
If you have a telescope, now is a great time to use it to study Mars. To see any details at all, you will need to use a high-power eyepiece.
Even though Mars is close, because it is physically small, the planet’s disc is tiny. It appears 80 times smaller than that of the full moon when viewed from Earth.
At the moment, we are getting good views of the red planet’s southern hemisphere, so look out for the south polar cap and dark-grey markings on its rusty surface.
A few weeks ago, I was able to photograph Mars from the University of Canterbury’s Mount John Observatory. Although the accompanying image was taken with a reasonably large observatory, it actually shows the kind of detail you can see with your eyes using a backyard telescope.
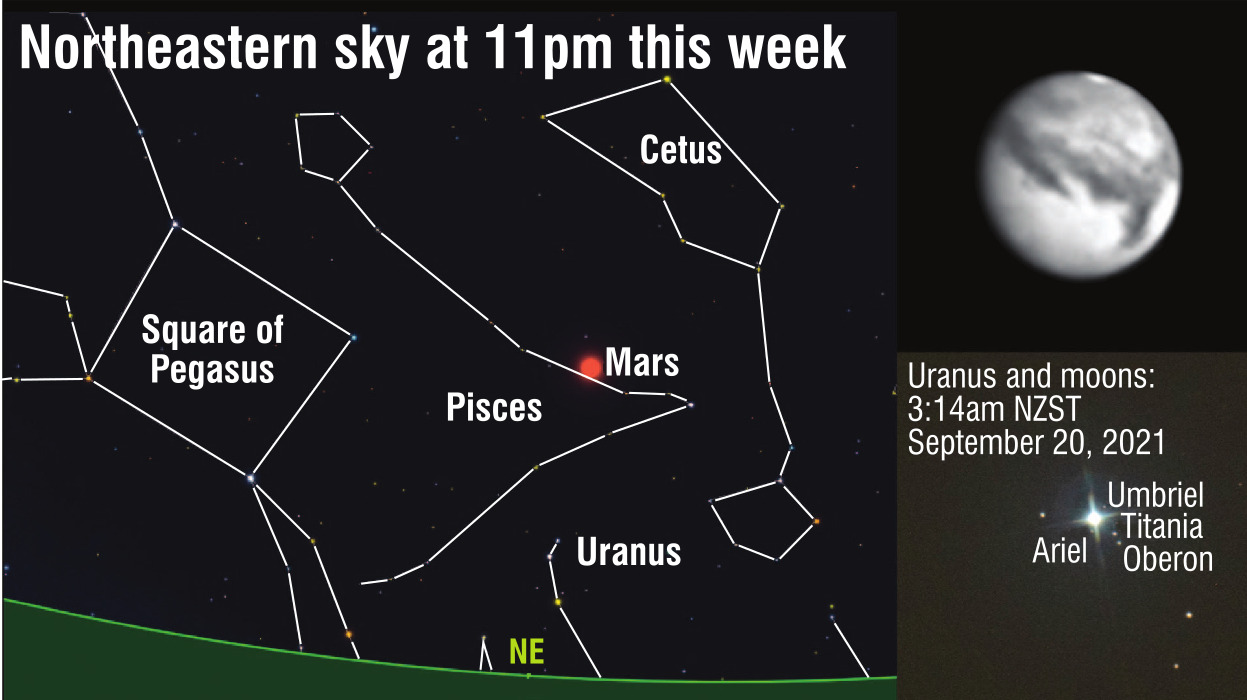
While some people with excellent eyesight can see Uranus, most of us require binoculars to locate it. Look for a noticeably green "star". Right now, the distance between Uranus and Earth is almost 3,000,000,000km.
During my last observing run at Mount John, I was able to photograph Uranus and four of its 27 moons. For reasons lost in the mists of time, are all named after characters from Shakespeare or Alexander Pope.












